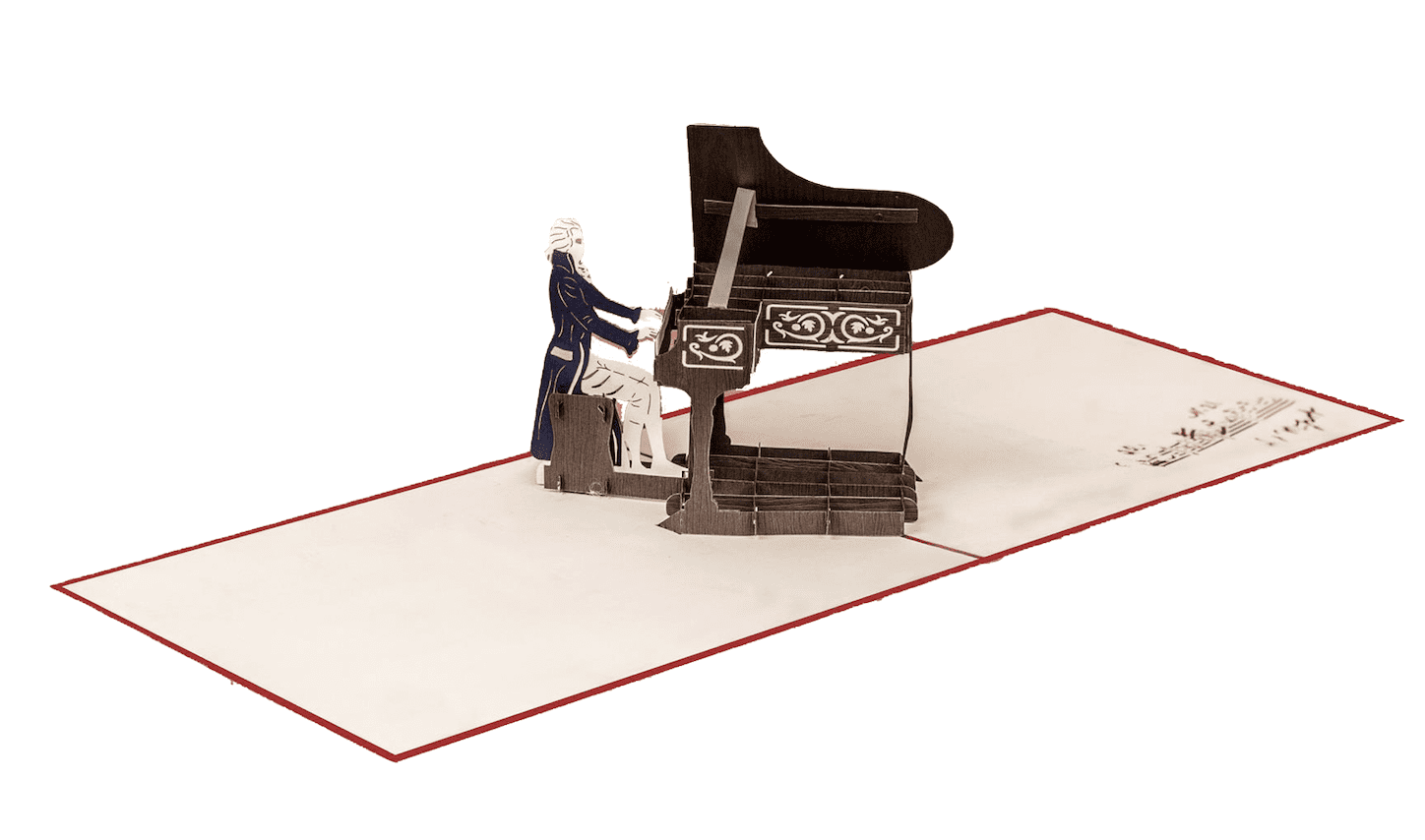
Description
Every student of music is familiar with at least a few works composed by Mozart. His works have been celebrated, studied, and performed since he began writing at the age of six, and have established his lasting fame as a prominent part of Western history. This gifted, multi-talented musician, like other geniuses, lived an exciting, turbulent life.
Messages and Quotes:
- Let’s make a little night music.
- Love, Love, Love, that is the soul of genius.
- Mozart is happiness before it has gotten defined. ~Arthur Miller
- Mozart is the musical Christ. ~Tchaikovsky
- His music is so beautiful as to entice angels down to earth. ~Franz Alexander von Kleis
- Listening to him, we cannot think of any possible improvement. ~George Szell
- It may be that when the angels go about their task praising God, they play only Bach. I am sure, however, that when they are together en famille they play Mozart. ~Karl Barth
- What a picture of a better world you have given us ~Franz Schubert
- When our kids were babies, my wife and I played them Salieri instead of Mozart, and now they’ve grown into jealous, brooding schemers. ~ Conan O’Brien
- Eine Kleine Nachtmusik (A Little Night Music)
This is a card for a birthday, for a musician, for a lover, for an opera singer or opera fan.
Mozart’s Storm of Style
~taken from Alex Ross’s essay in the New Yorker, on Mozart’s 250th birthday:
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, or Wolfgang Amadè Mozart, as he usually spelled his name, was a small man with a plain, pockmarked face, whose most striking feature was a pair of intense blue-gray eyes. When he was in a convivial mood, his gaze was said to be warm, even seductive. But he often gave the impression of being not entirely present, as if his mind were caught up in an invisible event. Portraits suggest a man aware of his separation from the world. In one, he wears a hard, distant look; in another, his face glows with sadness. In several pictures, his left eye droops a little, perhaps from fatigue. “As touchy as gunpowder,” one friend called him. Nonetheless, he was generally well liked.
An Urban character:
He was born in the archbishopric of Salzburg in 1756, and he died in the imperial capital of Vienna in 1791. He was an urban creature, and had almost nothing to say about the charms of nature. A product of the artisan classes—his ancestors were bookbinders, weavers, and masons—he adopted aristocratic fashions, going around Vienna in a gold-trimmed hat and a red coat with mother-of-pearl buttons. He was physically restless, quick-witted, sociable, flirtatious, and obscene; one of the more provocative items in his catalogue is a canon for six voices entitled “Leck mich im Arsch” [Kiss My Ass].
Emperor Joseph II was a fan of Mozart’s work, and, in 1787, to prevent “so rare a genius” from going abroad, he gave the composer a well-paying position that required little more than the writing of dances. In a letter to his father, Leopold, Mozart had warned that “the Viennese gentry, and in particular the Emperor, must not imagine that I am on this earth solely for the sake of Vienna.”
Child prodigy:
Mozart began composing at the age of five, but he was also a multi-instrumentalist, widely known for his ability to play the violin and the piano.
As a child prodigy, Mozart was advertised in London as “the most amazing Genius, that has appeared in any Age.” His father dubbed him “the miracle whom God allowed to be born in Salzburg.” Prince Kaunitz, Joseph II’s chief minister, said, “Such people come into the world once in a hundred years.”
Praise at this level, however justified, takes its toll on a man’s humility. Mozart, by his own admission, could be “as proud as a peacock,” and the Archbishop of Salzburg, whose service he quit in 1781, was not the only person who considered him “dreadfully conceited.” Conceit edges easily into paranoia, and Mozart was not immune. “I think that something is going on behind the scenes, and that doubtless here too I have enemies,” he wrote from Paris, in 1778. “Where, indeed, have I not had them?”
As he traces conspiracies, mocks the French, and extolls the Germans, he sounds remarkably like Richard Wagner. Later, in Vienna, Mozart clung to the idea that Antonio Salieri, the Imperial Kapellmeister, was plotting against him. Whether or not such intrigues existed — John Rice’s biography of the supposedly dastardly Salieri portrays him as a likable character and an imaginative composer — Mozart himself was not above politicking: when he applied for the job of second Kapellmeister, he pointedly observed that “the very capable Kapellmeister Salieri has never devoted himself to church music.”
Playfulness was Mozart’s saving grace.
His counterpart in modern times is perhaps George Gershwin, who was charming and self-infatuated in equal measure. Latter-day attempts to find a dark, brooding layer in Mozart’s psychology have been unconvincing. In his correspondence, he once or twice displays depressive symptoms — alluding to his “black thoughts,” describing sensations of coldness and emptiness — but context is all-important: in the first instance, he is begging for money, and in the second he is telling his wife, the demanding Constanze, how much he misses her.
Nor should too much be made of the fact that Mozart wrote to his dying father that death is the “true goal of our existence,” the “best and truest friend of mankind.” These sentiments were commonplace in a world where lives ended early and without warning. Of the seven children born to Leopold and Maria Anna Mozart, Wolfgang was one of two who survived infancy; only two of his own six children lived to adulthood. Against this backdrop, Mozart seems, if anything, indefatigably optimistic.
Golden Mean:
Leopold Mozart once said of his son, “Two opposing elements rule his nature, I mean, there is either too much or too little, never the golden mean.” Often, an artist sets forth in his work what he cannot achieve in life, and Mozart’s music is the empire of the golden mean.
Emotions:
Nicholas Kenyon, in his excellent new “Faber Pocket Guide to Mozart,” writes, “Other great composers have expressed the extremes of life: affirmation, despair, sensual pleasure, bleak emptiness, but only in Mozart can all these emotions co-exist in the space of a short phrase.”
Mozart inhabits a middle world where beauty surges in and ebbs away, where everything is contingent and nothing pure, where, as Henry James’s Madame Merle says, an envelope of circumstances encloses every human life. It is a place where genres meld; where concertos become operatic and arias symphonic; where comedy and tragedy, and the sensual and the sacred, are one.
Loss of innocence:
The scholar Scott Burnham recently observed that Mozart offers the “sound of the loss of innocence, the ever renewable loss of innocence.” There is no more potent subject for an artist, and it explains why Mozart remains so vivid a presence. As ever, the slow movement of the Piano Concerto No. 23 sends us into a wistful trance; the finale of the “Jupiter” Symphony wakes us up into a uniquely Mozartean kind of intelligent happiness; and the apocalyptic climax of “Don Giovanni” stirs our primal fear of being weighed in the balance and found wanting. The loss of innocence was Mozart’s, too. Like the rest of us, he had to live outside the complex paradise that he created in sound.
Greatest Works of Mozart:
Operas
- The Magic Flute (opera)
- Don Giovanni (opera)
- Marriage of Figaro (opera)
Concertos
- Piano Concerto No.27 in B-flat, K.595
- Piano Concerto No.21 in C, K.467
- Clarinet Concerto in A major, K.622
Symphonies
- Symphony No.39 in E flat, K.543
Choral Works
- Ave Verum Corpus K.618,
- Requiem K.626.
Other
- String Quintet in E-flat, K.614
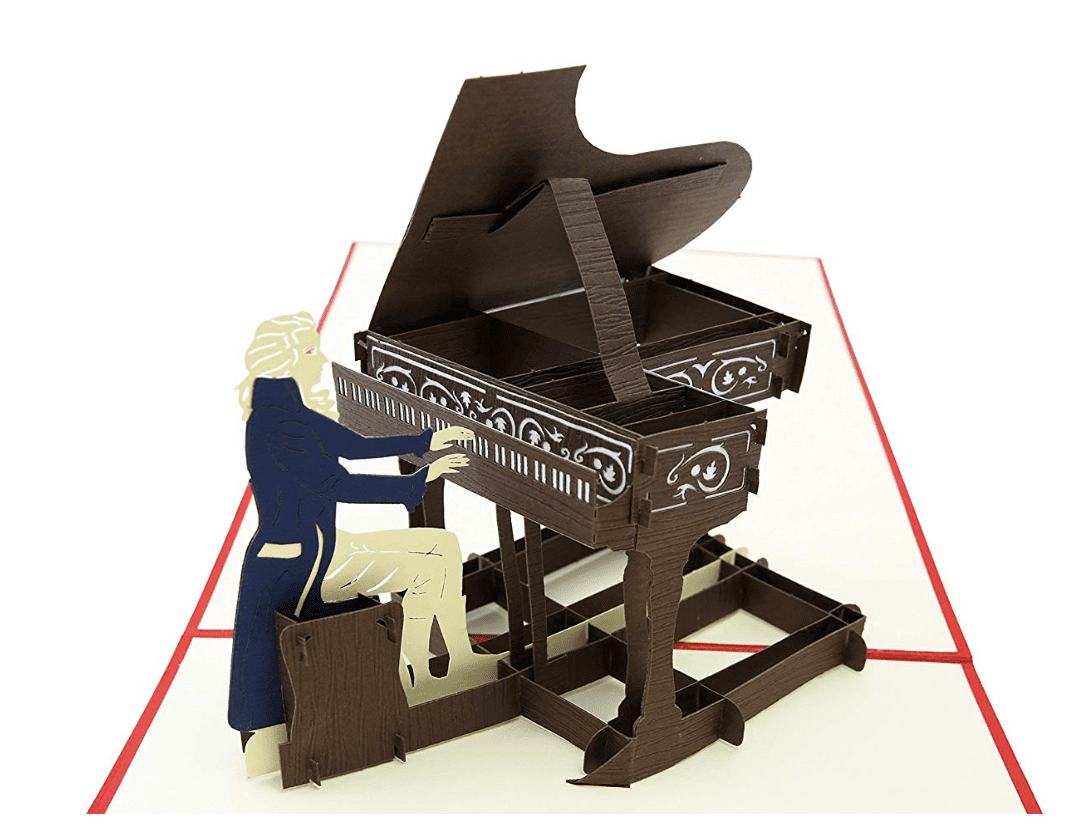
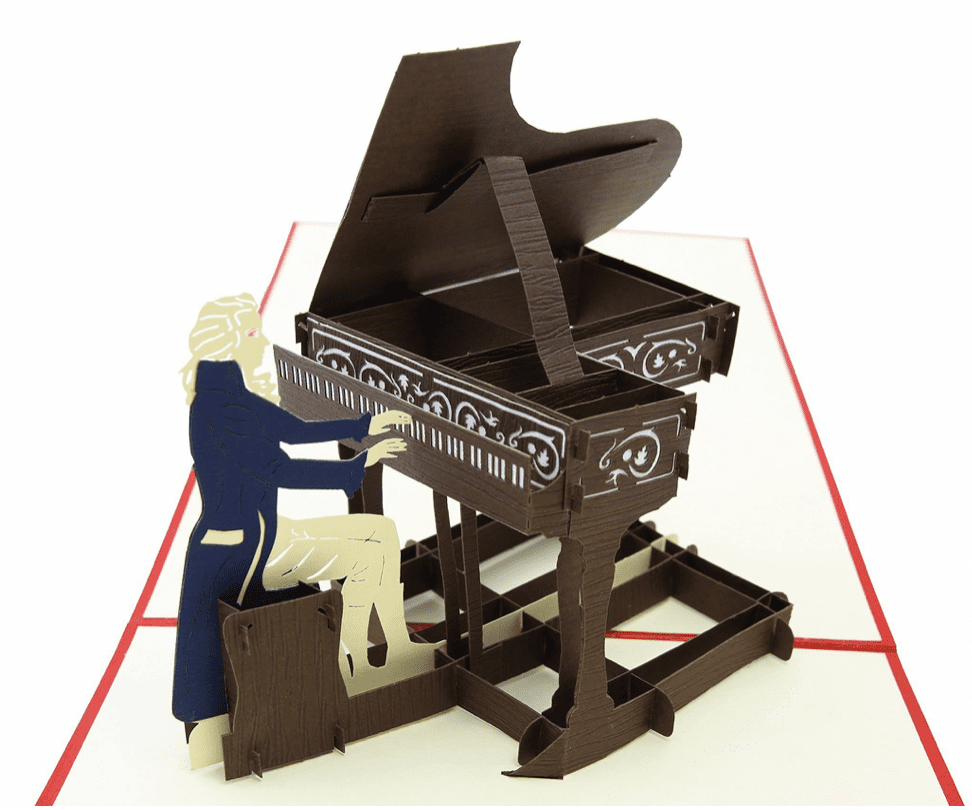
Mozart’s Piano:
Mozart’s piano was originally made by Anton Walter, one of the most famous Viennese piano makers of Mozart’s time. It is two octaves shorter than a modern piano, and is much lighter and smaller than modern pianos.
See also Gutenberg Printing Press.